Can AI and blockchain speed up vaccine distribution?
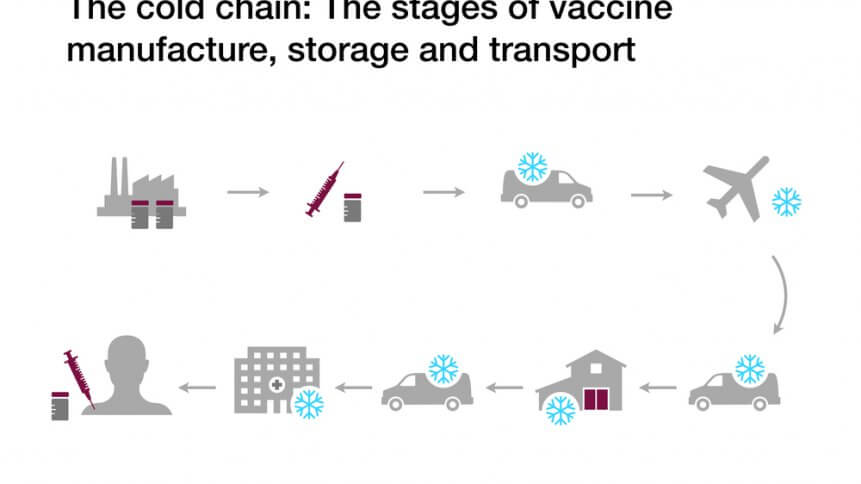
- The point of vaccine manufacture is just the start of a complex chain, as the logistics tied to the jab’s last-mile delivery are no less challenging
- Microsoft and IBM are tapping AI and blockchain, respectively, to facilitate vaccine delivery to billions of people across the planet
As the world faces its most pressing logistical challenge yet — vaccine distribution — countries are scrambling to make sure that jabs end up safely transmitted to patients, at scale, and on the quickest possible delivery schedule.
The impossible logistics of vaccine supply chains are by no means a novelty, however, and as has been the case on many occasions over the last year, technology seems to have impeccable solutions to offer.
Briefly put, a vaccine’s journey from its point of manufacture and all the way to a patient’s arm seems to be surrounded by an endless number of parameters to account for. As with most vaccines that typically require very low temperatures, it involves a cold chain.
That involves managing resources such as refrigerated containers and alcohol swabs, but also qualified staff. Worst yet, the vaccine’s lifespan shortens as soon as it leaves the freezer containers, and depending on the conditions the dose is kept it, can last from about a month to only a few hours.
Vaccine distribution made better with tech
According to data gathered by Bloomberg, more than 134 million doses have been administered across 73 countries with the latest rate roughly 4.74 million doses a day.
In the US, 43.1 million doses have been given out, according to a state-by-state tally. And the country holds a vaccination rate of 1,470,823 doses per day, on average. At this rate, it will take an estimated 10 months to cover 75% of the population with a two-dose vaccine. To accurately forecast demand for the vaccine is particularly important, as governments can’t afford to let doses go to waste.
YOU MIGHT LIKE

3 macro trends redrawing digitized supply chains in 2021
The World Economic Forum noted that blockchain technology allows multiple parties to manage and share a decentralized database. These parties can create and share a transparent source of data that can be mutually agreed upon.
Hence why blockchain might be the perfect infrastructure for supply chain management platforms as it covers two key pre-requisites requirements for building digital trust: it is not owned by anyone, and it provides a generic standardized protocol that all participants along the supply chain can join and share relevant data.
Data on the blockchain is also immutable, therefore existing information cannot be deleted, only appended, which consequently drives a higher level of accountability by each participant that writes new data.
As for artificial intelligence (AI), it can help in among others, demand forecasting, supply chain management and post-vaccination surveillance.
IBM has made available an open platform to facilitate vaccine delivery to billions of people across the planet by bringing together blockchain, data and AI, hybrid cloud, and security technologies.
Microsoft on the other hand mobilized its AI for Health data science team in the development of a comprehensive Covid-19 vaccine dashboard that tracks the distribution and administration worldwide, in each US state, and toward the federal goal of 100M vaccine doses in 100 days.








